Dual-Band vs Tri-Band Wi-Fi 6 Routers Explained
Dual-Band Gigabit Wi-Fi 6 Router vs Tri-Band Wi-Fi 6 Router: Choosing the Right Router for Your Needs
With the increasing number of devices in our homes, the demand for faster, more reliable, and versatile internet connections is at an all-time high. Wi-Fi 6 routers have become the standard for delivering high-speed internet with better efficiency, offering the latest Wi-Fi technology for seamless connectivity in homes and offices. but when it comes to choosing between dual-band and tri-band Wi-Fi 6 routers, the decision can be a bit daunting. In this article, we’ll delve into the differences between these two router types, exploring key features, use cases, and how they cater to different user requirements.
What is a Dual-Band Wi-Fi 6 Router?
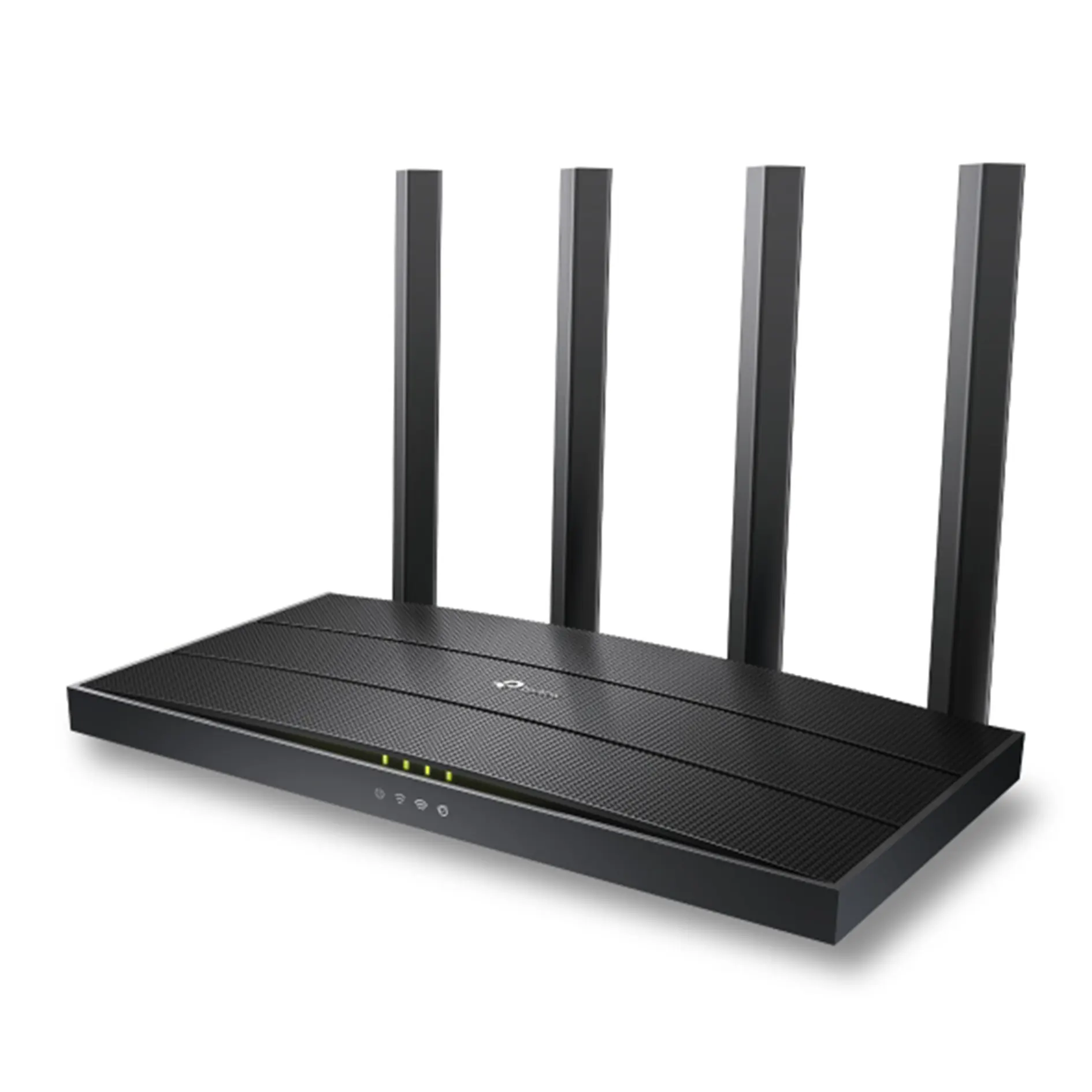
A dual-band Wi-Fi 6 router operates on two frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. These bands enable devices to connect at different speeds and ranges depending on their requirements.
Key Features of Dual-Band Wi-Fi 6 Routers:
Gigabit Speeds:
A dual-band router like the AX5400 Dual-Band Gigabit Wi-Fi 6 Router offers impressive speeds of up to 5400 Mbps, split across its two bands.
The 2.4 GHz band provides longer-range coverage with a speed of 574 Mbps, while the 5 GHz band delivers ultra-fast connections of up to 4.8 Gbps for bandwidth-heavy tasks like 8K streaming.
Efficient Connectivity:
Equipped with technologies like MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output) and OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access), dual-band routers efficiently manage multiple device connections, reducing network congestion.
Enhanced Features:
6 high-gain antennas with Beamforming technology ensure extensive coverage and stable connections.
Advanced security features like TP-Link’s HomeShield provide protection against cyber threats, safeguarding connected devices.
Convenience and Sharing:
USB ports, such as the USB 3.0 port in the AX5400, enable media sharing and private cloud creation.
Easy setup and management through apps like Tether simplify the user experience.
What is a Tri-Band Wi-Fi 6 Router?
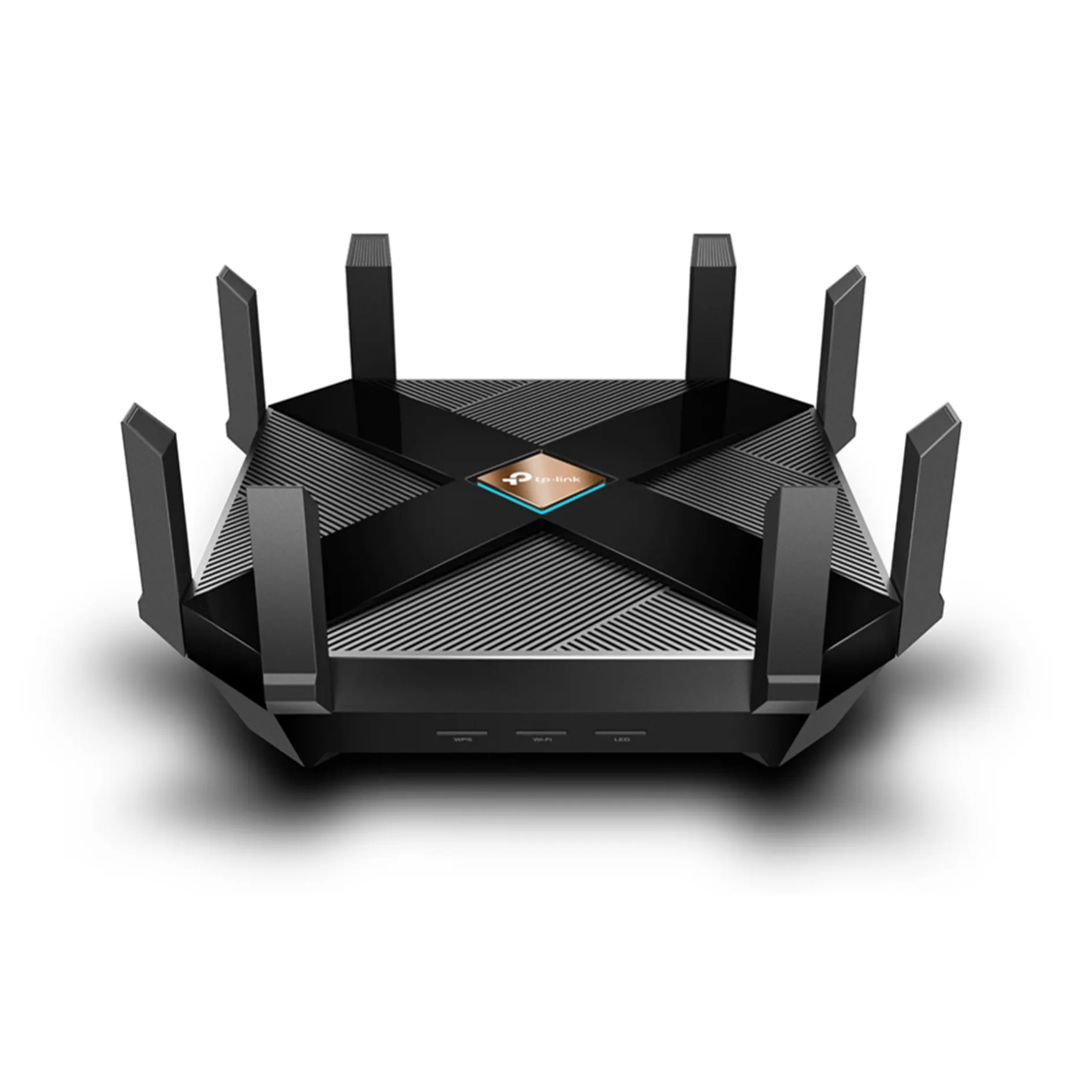
A tri-band Wi-Fi 6 router takes connectivity to the next level by introducing a third frequency band. Typically, this includes two 5 GHz bands and one 2.4 GHz band, allowing for more devices to connect simultaneously without interference.
Key Features of Tri-Band Wi-Fi 6 Routers:
Superior Speeds:
Routers like the AX3200 Tri-Band Wi-Fi 6 Router (ideal for advanced connectivity and larger homes) provide combined speeds of up to 3200 Mbps, divided among 1440 Mbps on one 5 GHz band, 1201 Mbps on the other 5 GHz band, and 574 Mbps on the 2.4 GHz band.
These speeds are ideal for activities requiring high bandwidth, such as gaming, 4K/8K streaming, and large file transfers.
Greater Capacity:
Tri-band routers excel in environments with many connected devices. By splitting traffic among three bands, they minimize congestion and ensure each device gets optimal bandwidth.
Extended Coverage:
Features like seven high-gain antennas and Beamforming technology ensure strong and stable connections across larger areas.
Enhanced Hardware:
A powerful CPU, such as the 1.5 GHz quad-core processor in the AX3200, ensures smooth operation of multiple devices and high-speed data transmission.
Flexible Connectivity Options:
Tri-band routers offer extensive wired connectivity options, including multiple Gigabit Ethernet ports and USB ports, enhancing their versatility for home and office use.
Advanced Security:
With WPA3 encryption, tri-band routers provide improved network security, protecting user data from potential threats.
Key Differences Between Dual-Band and Tri-Band Routers
1. Number of Frequency Bands
Dual-Band Routers: Two frequency bands (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz).
Tri-Band Routers: Three frequency bands (2.4 GHz and two 5 GHz bands).
2. Device Support and Network Congestion
Dual-Band: Suitable for households with a moderate number of devices. Can handle streaming, gaming, and browsing simultaneously, but may face congestion when multiple high-bandwidth activities occur.
Tri-Band: Designed for larger households or small offices with many devices. The additional 5 GHz band ensures smoother performance during heavy usage.
3. Speed Distribution
Dual-Band: Focused on balancing range and speed between the two bands. Ideal for standard internet usage and streaming.
Tri-Band: Offers higher aggregate speeds, with one 5 GHz band often dedicated to bandwidth-intensive tasks like gaming or 4K streaming.
4. Price Point
Dual-Band: Generally more affordable, making it a cost-effective choice for average users.
Tri-Band: Higher price tag due to advanced features and greater capacity.
5. Use Case
Dual-Band: Best suited for small to medium-sized homes or users with fewer devices.
Tri-Band: Perfect for larger homes, smart homes with numerous IoT devices, or users with heavy streaming and gaming requirements.
Use Case Scenarios
When to Choose a Dual-Band Router:
Small to Medium Homes:
A dual-band router is sufficient for homes with fewer rooms and devices.
Moderate Internet Usage:
If your household uses the internet for browsing, streaming, and occasional gaming, a dual-band router will meet your needs.
Budget-Friendly Option:
Dual-band routers are cost-effective, making them ideal for users on a budget.
When to Choose a Tri-Band Router:
Large Homes or Offices:
The extended coverage and additional band make tri-band routers suitable for larger spaces.
Heavy Internet Usage:
If your household frequently streams 4K/8K content, plays online games, or downloads large files, a tri-band router is the better option.
Smart Home Integration:
For homes with numerous IoT devices, tri-band routers provide the bandwidth needed to keep everything connected seamlessly.
Conclusion
Choosing between a dual-band and tri-band Wi-Fi 6 router depends on your specific needs and internet usage patterns. This Wi-Fi router buying guide will help you navigate the differences, making selecting the right router for your home or office simpler. While dual-band routers like the AX5400 offer excellent speeds, coverage, and features at a reasonable price, tri-band routers like the AXE5700 provide superior capacity, faster speeds, and better performance for high-demand environments.
For average households, a dual-band router is more than capable of handling everyday tasks. However, for tech enthusiasts, gamers, or users with large homes and many connected devices, investing in a tri-band router ensures optimal performance and future-proofing. By understanding the differences and evaluating your requirements, you can make an informed decision that enhances your internet experience.


















